Debugging HTTP applications with per-route metrics
This demo is of a Ruby application that helps you manage your bookshelf. It consists of multiple microservices and uses JSON over HTTP to communicate with the other services. There are three services:
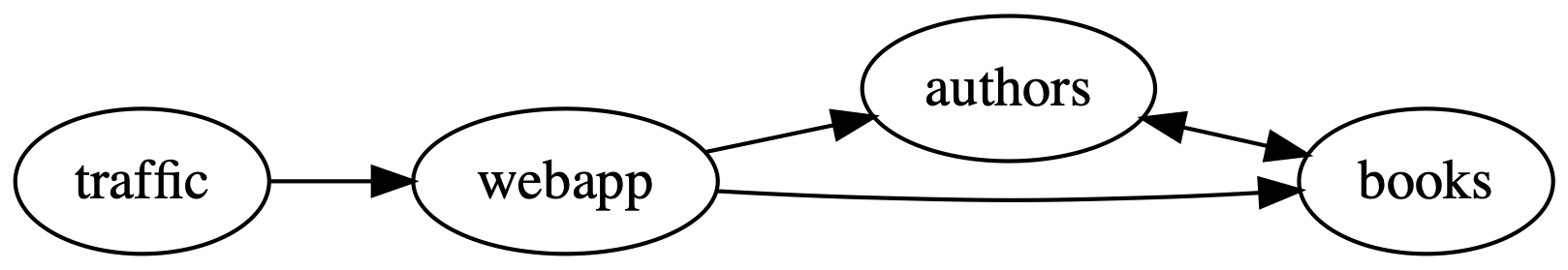
webapp: the frontend
authors: an API to manage the authors in the system
books: an API to manage the books in the system
For demo purposes, the app comes with a simple traffic generator. The overall topology looks like this:
Prerequisites
To use this guide, you’ll need to have Linkerd installed on your cluster. Follow the Installing Linkerd Guide if you haven’t already done this.
Install the app
To get started, let’s install the books app onto your cluster. In your local terminal, run:
kubectl create ns booksapp && \
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSfL https://run.linkerd.io/booksapp.yml \
| kubectl -n booksapp apply -f -
This command creates a namespace for the demo, downloads its Kubernetes resource
manifest and uses kubectl to apply it to your cluster. The app comprises the
Kubernetes deployments and services that run in the booksapp namespace.
Downloading a bunch of containers for the first time takes a little while. Kubernetes can tell you when all the services are running and ready for traffic. Wait for that to happen by running:
kubectl -n booksapp rollout status deploy webapp
You can also take a quick look at all the components that were added to your cluster by running:
kubectl -n booksapp get all
Once the rollout has completed successfully, you can access the app itself by
port-forwarding webapp locally:
kubectl -n booksapp port-forward svc/webapp 7000 >/dev/null &
(We redirect to /dev/null just so you don’t get flooded with “Handling
connection” messages for the rest of the exercise.)
Open http://localhost:7000/ in your browser to see the frontend.
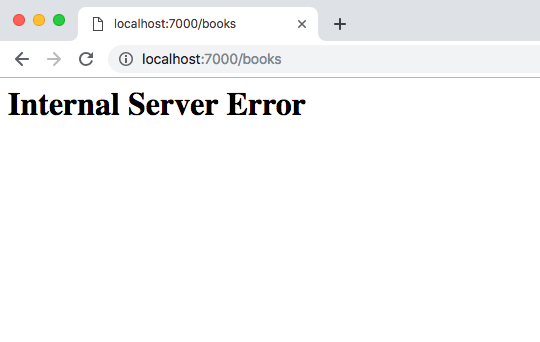
Unfortunately, there is an error in the app: if you click Add Book, it will fail 50% of the time. This is a classic case of non-obvious, intermittent failure—the type that drives service owners mad because it is so difficult to debug. Kubernetes itself cannot detect or surface this error. From Kubernetes’s perspective, it looks like everything’s fine, but you know the application is returning errors.
Add Linkerd to the service
Now we need to add the Linkerd data plane proxies to the service. The easiest option is to do something like this:
kubectl get -n booksapp deploy -o yaml \
| linkerd inject - \
| kubectl apply -f -
This command retrieves the manifest of all deployments in the booksapp
namespace, runs them through linkerd inject, and then re-applies with
kubectl apply. The linkerd inject command annotates each resource to specify
that they should have the Linkerd data plane proxies added, and Kubernetes does
this when the manifest is reapplied to the cluster. Best of all, since
Kubernetes does a rolling deploy, the application stays running the entire time.
(See Automatic Proxy Injection for more details
on how this works.)
Debugging
Let’s use Linkerd to discover the root cause of this app’s failures. We can use
the stat-inbound command to see the success rate of the webapp deployment:
linkerd viz -n booksapp stat-inbound deploy/webapp
NAME SERVER ROUTE TYPE SUCCESS RPS LATENCY_P50 LATENCY_P95 LATENCY_P99
webapp [default]:4191 [default] 100.00% 0.30 4ms 9ms 10ms
webapp [default]:4191 probe 100.00% 0.60 0ms 1ms 1ms
webapp [default]:7000 probe 100.00% 0.30 2ms 2ms 2ms
webapp [default]:7000 [default] 75.66% 8.22 18ms 65ms 93ms
This shows us inbound traffic statistics. In other words, we see that the webapp is receiving 8.22 requests per second on port 7000 and that only 75.66% of those requests are successful.
To dig into this further and find the root cause, we can look at the webapp’s outbound traffic. This will tell us about the requests that the webapp makes to other services.
linkerd viz -n booksapp stat-outbound deploy/webapp
NAME SERVICE ROUTE TYPE BACKEND SUCCESS RPS LATENCY_P50 LATENCY_P95 LATENCY_P99 TIMEOUTS RETRIES
webapp books:7002 [default] 77.36% 7.95 25ms 48ms 176ms 0.00% 0.00%
└──────────────────► books:7002 77.36% 7.95 15ms 44ms 64ms 0.00%
webapp authors:7001 [default] 100.00% 3.53 26ms 72ms 415ms 0.00% 0.00%
└──────────────────► authors:7001 100.00% 3.53 16ms 52ms 91ms 0.00%
We see that webapp sends traffic to both the books service and the authors service and that the problem seems to be with the traffic to the books service.
HTTPRoute
We know that the webapp component is getting failures from the books component,
but it would be great to narrow this down further and get per route metrics. To
do this, we take advantage of the Gateway API and define a set of HTTPRoute
resources, each attached to the books Service by specifying it as their
parent_ref.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
kind: HTTPRoute
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: books-list
namespace: booksapp
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: books
group: core
kind: Service
port: 7002
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: Exact
value: "/books.json"
---
kind: HTTPRoute
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: books-create
namespace: booksapp
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: books
group: core
kind: Service
port: 7002
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: Exact
value: "/books.json"
method: POST
---
kind: HTTPRoute
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: books-delete
namespace: booksapp
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: books
group: core
kind: Service
port: 7002
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: RegularExpression
value: "/books/\\\d+.json"
method: DELETE
EOF
We can then check that these HTTPRoutes have been accepted by their parent Service by checking their status subresource:
kubectl -n booksapp get httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io \
-ojsonpath='{.items[*].status.parents[*].conditions[*]}' | jq .
Notice that the Accepted and ResolvedRefs conditions are True.
{
"lastTransitionTime": "2024-08-03T01:38:25Z",
"message": "",
"reason": "Accepted",
"status": "True",
"type": "Accepted"
}
{
"lastTransitionTime": "2024-08-03T01:38:25Z",
"message": "",
"reason": "ResolvedRefs",
"status": "True",
"type": "ResolvedRefs"
}
[...]
With those HTTPRoutes in place, we can look at the outbound stats again:
linkerd viz -n booksapp stat-outbound deploy/webapp
NAME SERVICE ROUTE TYPE BACKEND SUCCESS RPS LATENCY_P50 LATENCY_P95 LATENCY_P99 TIMEOUTS RETRIES
webapp authors:7001 [default] 100.00% 2.80 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► authors:7001 100.00% 2.80 16ms 45ms 49ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-list HTTPRoute 100.00% 1.43 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 1.43 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-create HTTPRoute 54.27% 2.73 27ms 207ms 441ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 54.27% 2.73 14ms 152ms 230ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-delete HTTPRoute 100.00% 0.72 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 0.72 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
This tells us that it is requests to the books-create HTTPRoute which have
been failing.
Retries
As it can take a while to update code and roll out a new version, let’s tell
Linkerd that it can retry requests to the failing endpoint. This will increase
request latencies, as requests will be retried multiple times, but not require
rolling out a new version. Add a retry annotation to the books-create
HTTPRoute which tells Linkerd to retry on 5xx responses:
kubectl -n booksapp annotate httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io/books-create \
retry.linkerd.io/http=5xx
We can then see the effect of these retries:
linkerd viz -n booksapp stat-outbound deploy/webapp
NAME SERVICE ROUTE TYPE BACKEND SUCCESS RPS LATENCY_P50 LATENCY_P95 LATENCY_P99 TIMEOUTS RETRIES
webapp books:7002 books-create HTTPRoute 73.17% 2.05 98ms 460ms 492ms 0.00% 34.22%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 48.13% 3.12 29ms 93ms 99ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-list HTTPRoute 100.00% 1.50 25ms 48ms 49ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 1.50 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-delete HTTPRoute 100.00% 0.73 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 0.73 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
webapp authors:7001 [default] 100.00% 2.98 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► authors:7001 100.00% 2.98 16ms 44ms 49ms 0.00%
Notice that while the success rate of individual requests to the books backend
on the books-create route only have a success rate of about 50%, the overall
success rate on that route has been raised to 73% due to retries. We can also
see that 34.22% of the requests on this route are retries and that the improved
success rate has come at the expense of additional RPS to the backend and
increased overall latency.
By default, Linkerd will only attempt 1 retry per failure. We can improve success rate further by increasing this limit to allow more than 1 retry per request:
kubectl -n booksapp annotate httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io/books-create \
retry.linkerd.io/limit=3
Looking at the stats again:
linkerd viz -n booksapp stat-outbound deploy/webapp
NAME SERVICE ROUTE TYPE BACKEND SUCCESS RPS LATENCY_P50 LATENCY_P95 LATENCY_P99 TIMEOUTS RETRIES
webapp books:7002 books-delete HTTPRoute 100.00% 0.75 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 0.75 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
webapp authors:7001 [default] 100.00% 2.92 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► authors:7001 100.00% 2.92 18ms 46ms 49ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-create HTTPRoute 92.78% 1.62 111ms 461ms 492ms 0.00% 47.28%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 48.91% 3.07 42ms 179ms 236ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-list HTTPRoute 100.00% 1.45 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 1.45 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
We see that these additional retries have increased the overall success rate on this route to 92.78%.
Timeouts
Linkerd can limit how long to wait before failing outgoing requests to another
service. For the purposes of this demo, let’s set a 15ms timeout for calls to
the books-create route:
kubectl -n booksapp annotate httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io/books-create \
timeout.linkerd.io/request=15ms
(You may need to adjust the timeout value depending on your cluster – 15ms should definitely show some timeouts, but feel free to raise it if you’re getting so many that it’s hard to see what’s going on!)
We can see the effects of this timeout by running:
linkerd viz -n booksapp stat-outbound deploy/webapp
NAME SERVICE ROUTE TYPE BACKEND SUCCESS RPS LATENCY_P50 LATENCY_P95 LATENCY_P99 TIMEOUTS RETRIES
webapp authors:7001 [default] 100.00% 2.85 26ms 49ms 370ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► authors:7001 100.00% 2.85 19ms 49ms 86ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-create HTTPRoute 78.90% 1.82 45ms 449ms 490ms 21.10% 47.34%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 41.55% 3.45 24ms 134ms 227ms 11.11%
webapp books:7002 books-list HTTPRoute 100.00% 1.40 25ms 47ms 49ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 1.40 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
webapp books:7002 books-delete HTTPRoute 100.00% 0.70 25ms 48ms 50ms 0.00% 0.00%
└─────────────────────► books:7002 100.00% 0.70 12ms 24ms 25ms 0.00%
We see that 21.10% of the requests are hitting this timeout.
Clean Up
To remove the books app and the booksapp namespace from your cluster, run:
kubectl delete ns booksapp


